Introduction
Assistive technology is transforming how employees with dyslexia overcome workplace challenges, enabling them to excel and contribute their best. These tools empower individuals to overcome challenges related to reading, writing, and organization, enabling them to perform at their best. For HR professionals, investing in such technology isn’t just about compliance; it’s about fostering inclusion and unlocking the potential of a neurodiverse workforce.
This blog explores the most effective assistive tools for employees with dyslexia, how they work, and how HR teams can implement them to create a more inclusive workplace.
Why Assistive Technology Matters
Dyslexic employees often face barriers that traditional workplace tools don’t address. Assistive technology bridges this gap, helping employees:
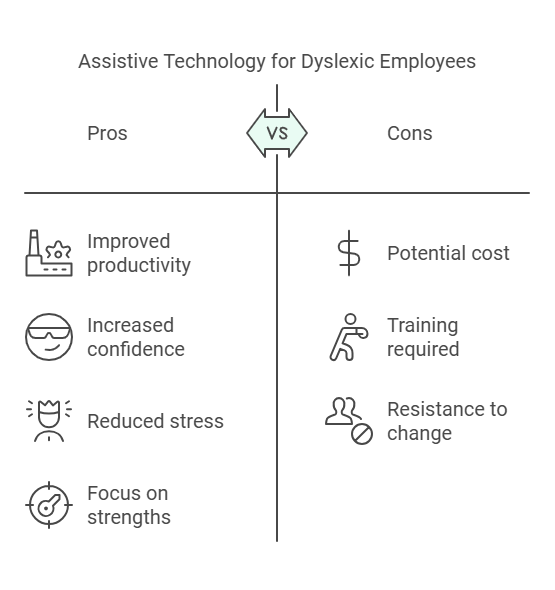
- Improve productivity and confidence.
- Reduce stress caused by tasks requiring heavy reading or writing.
- Focus on their strengths, such as creativity and problem-solving.
By integrating these tools, organizations can enhance employee satisfaction and retention.
For broader strategies on supporting dyslexic employees, check out “Creating a Dyslexia-Friendly Workplace: Tips for HR Professionals.”
Top Assistive Technologies for Dyslexic Employees
1. Speech-to-Text Tools
Speech-to-text software converts spoken words into written text, making it easier for employees to draft emails, reports, or notes.
- Popular Options: Dragon NaturallySpeaking, Google Docs Voice Typing.
- Best For: Employees who struggle with spelling or typing speed.
2. Text-to-Speech Software
These tools read digital text aloud, helping employees process written information more effectively.
- Popular Options: NaturalReader, Kurzweil 3000, Microsoft Immersive Reader.
- Best For: Employees who find reading lengthy documents challenging.
3. Mind Mapping Apps
Mind mapping tools help dyslexic employees organize their thoughts visually, making brainstorming and planning more intuitive.
- Popular Options: MindMeister, XMind, Coggle.
- Best For: Creative thinkers who need a non-linear way to outline ideas.
4. Dyslexia-Friendly Fonts and Overlays
Specialized fonts like Dyslexie and OpenDyslexic reduce visual stress, while color overlays help improve reading clarity.
- Implementation: Provide software with font options or physical overlays for printed materials.
- Best For: Employees with visual processing difficulties.
5. Time Management and Organizational Apps
These tools support employees with planning, scheduling, and task prioritization.
- Popular Options: Trello, Todoist, Microsoft To Do.
- Best For: Employees who struggle with time management or task organization.
Implementing Assistive Technology in the Workplace
Step 1: Assess Employee Needs
Start by identifying specific challenges your dyslexic employees face. Conduct one-on-one meetings or anonymous surveys to gather insights.
Step 2: Provide Training and Support
Introduce assistive tools with clear instructions and training sessions. Ensure IT teams are equipped to troubleshoot issues.
Step 3: Normalize Usage
Promote these tools as resources for everyone, not just for employees with dyslexia, to reduce stigma and encourage broader adoption.
For more insights into fostering inclusivity, read “Understanding Dyslexia: How It Impacts the Modern Workplace.”
Success Stories: Assistive Technology in Action
Case Study 1: Using Speech-to-Text for Reports
A dyslexic employee in a legal firm struggled with drafting lengthy case reports. With Dragon NaturallySpeaking, they reduced report preparation time by 50%, freeing them to focus on analysis and client interactions.
Case Study 2: Visual Learning with Mind Mapping
A project manager adopted MindMeister for team planning. They found it easier to visualize timelines and responsibilities, improving team communication and project outcomes.
Overcoming Common Barriers
Cost Concerns
Many assistive tools, such as Microsoft’s built-in accessibility features, are free or low-cost. Employers can also explore grants or tax incentives for workplace accommodations.
Resistance to Adoption
Some employees may hesitate to use new tools. Encourage adoption by highlighting success stories and offering ongoing support.
Compatibility Issues
Ensure assistive tools are compatible with your organization’s existing software and hardware to avoid disruptions.
The Broader Impact of Assistive Technology
Assistive tools benefit not only dyslexic employees but the entire workforce. They improve accessibility, encourage innovation, and demonstrate the organization’s commitment to inclusivity.
Learn more about how dyslexia contributes to workplace success in “The Benefits of Embracing Neurodiversity: Dyslexia as an Asset in the Workplace.”
Conclusion
Assistive technology is a powerful resource for creating an inclusive workplace where dyslexic employees can thrive. By providing the right tools, organizations can reduce barriers, enhance productivity, and foster a culture of innovation.
Call to Action
Interested in learning more about dyslexia and inclusion? Read “Training Managers to Support Dyslexic Employees: A Step-by-Step Guide” for insights into equipping your leadership team with the knowledge they need.
Featured image by istockphoto.com


